WordPress is one of the most popular content management systems (CMS) in the world, and for good reason—it’s user-friendly, versatile, and scalable. However, for beginners, the different components of a WordPress website can seem overwhelming. In this article, we’ll break down the key elements of WordPress websites, including Pages, Posts, Portfolio, Users, and more, to help you understand how they work together.
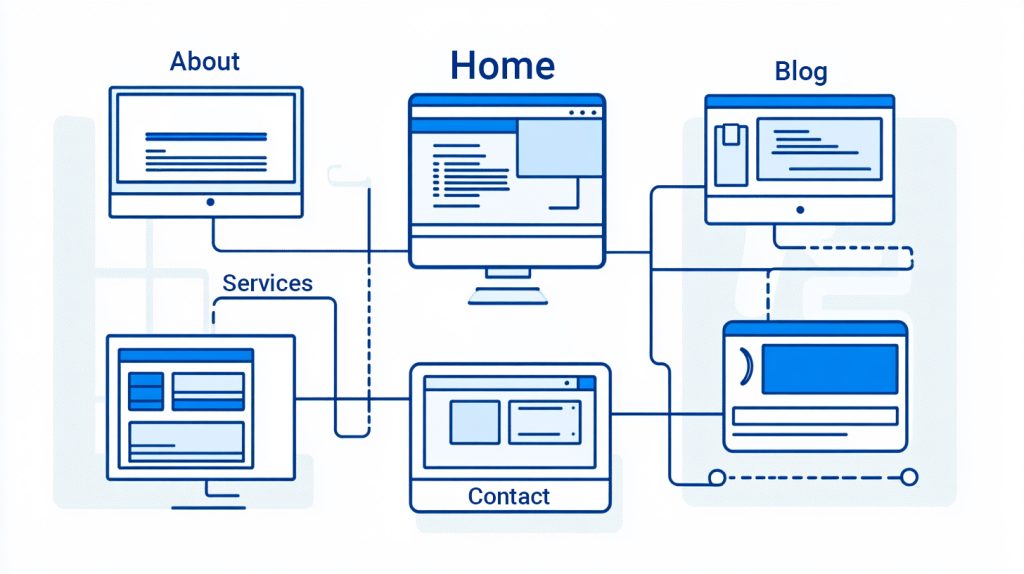
Pages: The Building Blocks of Your Website
Pages are static content types that form the core of your website’s structure. They are ideal for content that doesn’t change frequently, such as:
- Home Page: The main landing page.
- About Us: A section explaining who you are.
- Contact Page: A place for visitors to reach you.
- Services or Products: Showcasing what you offer.
Key Characteristics of Pages:
- They are hierarchical, meaning you can create parent and child pages.
- They don’t display a publication date.
- They are typically organized into menus for easy navigation.

Posts: Dynamic Content for Blogs and News
Posts are time-sensitive entries that are displayed in reverse chronological order, making them perfect for blogs, news updates, or any regularly updated content.
Key Characteristics of Posts:
- Organized by categories and tags.
- Display publication dates, making them suitable for timely content.
- Automatically appear in your blog feed unless otherwise configured.
Posts are also great for improving SEO since regular updates signal search engines that your website is active.

Portfolio: Showcasing Your Work
If you’re a creative professional, WordPress offers a Portfolio feature (available in some themes and plugins). Portfolios are designed to highlight your projects, whether you’re a photographer, designer, writer, or artist.
Key Characteristics of Portfolios:
- Each project can include images, descriptions, and links.
- Often grouped by project categories or tags.
- Displays beautifully in grid or masonry layouts depending on the theme.

Users: Managing Website Access
WordPress allows multiple user roles, each with different permissions. This is particularly useful for collaborative websites or businesses.
User Roles in WordPress:
- Administrator: Full access to the site.
- Editor: Can publish and manage all content.
- Author: Can publish and manage their own posts.
- Contributor: Can write and edit their posts but can’t publish them.
- Subscriber: Can only manage their own profile.
Proper user management ensures that your website remains secure and organized.
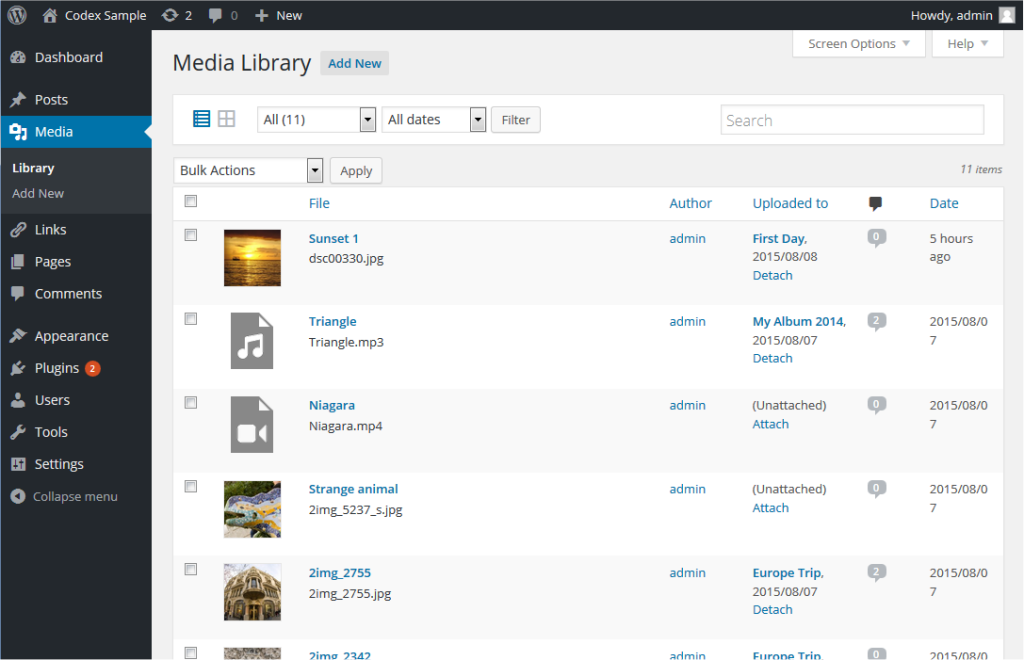
Media Library: Centralizing Your Assets
The Media Library houses all the images, videos, documents, and other files uploaded to your site. You can reuse media assets across your pages and posts, saving time and effort.
Tips for Using the Media Library:
- Optimize image sizes for faster loading times.
- Use descriptive file names to improve accessibility and SEO.
- Organize media into folders using plugins if necessary.
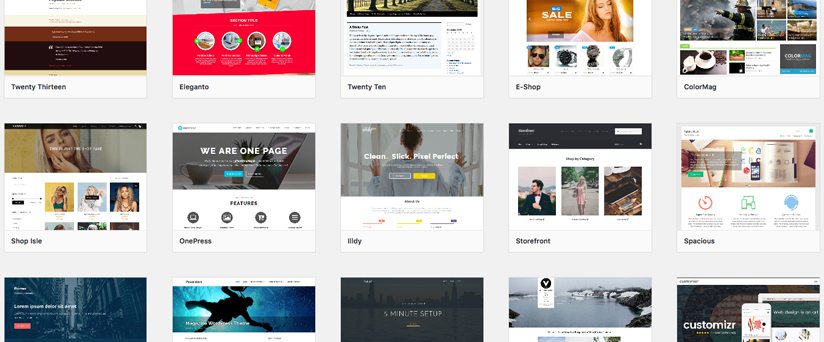
Themes and Plugins: Customizing Functionality
While not part of the content structure, Themes and Plugins play a critical role in shaping your website.
- Themes: Control the design and layout.
- Plugins: Add additional functionality (e.g., SEO tools, contact forms, e-commerce features).
Widgets and Menus: Enhancing Navigation
Widgets are small blocks of content that can be placed in designated areas (like sidebars or footers). Common widgets include search bars, recent posts, or social media links.
Menus, on the other hand, are used to organize and display your site’s navigation links. Both contribute to a seamless user experience.
Custom Post Types: Tailored Content
Beyond default content types, WordPress allows the creation of custom post types for specific purposes. Examples include:
- Testimonials: Customer feedback.
- Events: Calendar entries.
- Products: Items for e-commerce sites.
Custom post types add flexibility to your site’s functionality and structure.

Conclusion: A Cohesive System
WordPress’s structure may seem complex at first, but its components work harmoniously to create versatile, functional websites. Whether you’re building a simple blog or a professional portfolio, understanding how Pages, Posts, Portfolio, Users, and other elements fit together is essential for success.
By mastering these building blocks, you can fully harness the power of WordPress to create a website that meets your needs and engages your audience.

